|
USB 3.1: The Need for Speed
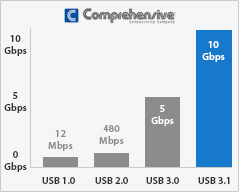
On July 31st 2013, a faster transfer mode “SuperSpeed USB” was released. This only became widely known to many a few months ago with the release of Apple®’s new Macbook. SuperSpeed USB refers to USB 3.1 Gen 1 because it uses the same data signaling rate as USB 3.0 at 5Gbps. The fastest USB transfer mode “SuperSpeedPlus USB” refers to USB 3.1 Gen 2, and increases the data signaling rate to 10Gbps. USB 3.1 is backwards compatible with USB 3.0 and USB 2.0. For instance, you may have a device that supports USB 3.1 speeds but if the computer only supports up to USB 2.0, you can only obtain speeds of the lower version.
USB Type-C: A smaller, reversible USB Connector
USB Type-C offers a new low profile design. The new smaller size is similar to the size of USB 2.0 Micro-B. The Type-C design is more robust and durable compared to the previous versions of USB connectors. USB Type-C is now reversible or flip-able similar to the Apple® Lightning connector. The Type-C connector connects to both sources and devices. Type-C can be adapted to Type A and Type B connections.
All USB solutions are required to support Default USB Power to the correct USB product. USB Type-C supports current ranges 1.5A, 3A @ 5V, and 5A @ 20V. USB Type-C supports USB Power Delivery up to 100W of power, as opposed to the older standard 10W. This means manufacturers could power Laptops and Monitors though the USB Type-C connection.
USB Type-C is a single connector platform model which includes but is not limited to Power, Display, Network, Storage, Audio, Mouse, and Keyboard. USB Type-C supports USB Alternate Mode, which allows USB Type-C devices to transmit non-USB data, such as DisplayPort or HDMI data. This would allow you to power a monitor and transfer data via USB 3.1 over the same cable similar to Apple’s Thunderbolt Display. Both DisplayPort and MHL have already announced support for USB Alternate Mode. Take a look at the Type-C connector below compared to two current popular USB connector types:
|