A network is a collection of computers, servers, mainframes, network devices, peripherals, or other devices connected to one another to allow the sharing of data. An example of a network is the Internet, which connects millions of people all over the world. A network enables devices and endpoints to be connected to each other on a local area network (LAN) or to a larger network, such as the internet or a private wide area network (WAN). This is an essential function for service providers, businesses and consumers worldwide to share resources, use or offer services, and communicate. Networking facilitates everything from telephone calls to text messaging to streaming video to the internet of things (IoT).
Switches, routers, and wireless access points are the essential networking basics. Through them, devices connected to your network can communicate with one another and with other networks, like the Internet. Switches, routers, and wireless access points perform very different functions in a network. Peripherals which include mice, printers, card readers, network patch cables, fiber optic patch cables, and more are commonly used in or around a network with various hardware.
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as a home, school, office building, or closely positioned group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is a node. Wired LANs are most likely based on Ethernet technology.
What is a WAN (wide area network)?
A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a large geographic area such as a city, country, or spans even intercontinental distances. A WAN uses a communications channel that combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables, and air waves. A WAN often makes use of transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone companies. WAN technologies generally function at the lower three layers of the OSI reference model: the physical layer, the data link layer, and the network layer.
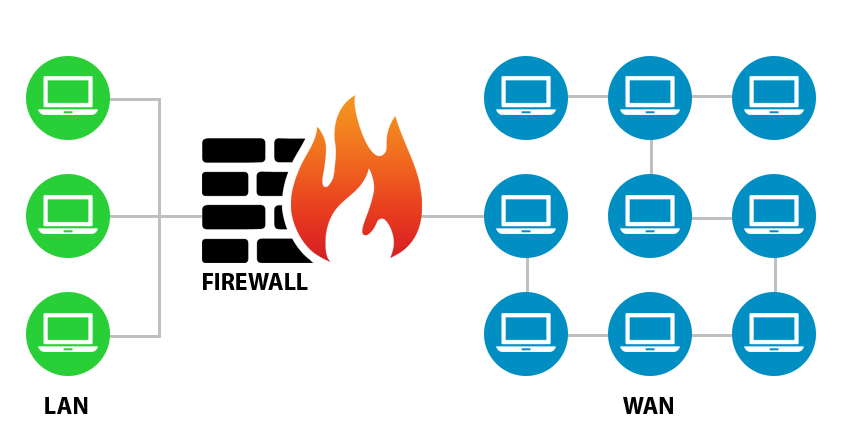
What is a firewall?
A firewall is a network device for controlling network security and access rules. Firewalls are typically configured to reject access requests from unrecognized sources while allowing actions from recognized ones. The vital role firewalls play in network security grows in parallel with the constant increase in cyber-attacks.
What is a VPN (virtual private network)?
A virtual private network (VPN) is an overlay network in which some of the links between nodes are carried by open connections or virtual circuits in some larger network (e.g., the Internet) instead of by physical wires. The data link layer protocols of the virtual network are said to be tunneled through the larger network when this is the case. One common application is secure communications through the public Internet, but a VPN need not have explicit security features, such as authentication or content encryption. VPNs, for example, can be used to separate the traffic of different user communities over an underlying network with strong security features.
What is a Wi-Fi Network?
A wireless network allows devices to stay connected to the network but roam untethered to any wires. Access points amplify Wi-Fi signals, so a device can be far from a router but still be connected to the network. When you connect to a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe, a hotel, an airport lounge, or another public place, you're connecting to that business's wireless network.
What is a wireless access point?
A wireless access point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to a wired network. It is simpler and easier to install WAPs to connect all the computers or devices in your network than to use wires and cables.
Wired networking requires the use of a physical medium for transport between nodes. Copper-based Ethernet cabling, popular due to its low cost and durability, is commonly used for digital communications in businesses and homes. Alternatively, optical fiber is used to transport data over greater distances and at faster speeds, but it has several tradeoffs, including higher costs and more fragile components.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ethernet ports are found on almost all laptops/PCs and netbooks even on those 8 years old | Need to Use cable which can be unsightly, difficult to run and expensive. |
| Wired networks are faster than Wireless. Data rates were periodically increased from the original 10 megabits per second, to 1gigabits per second. Most home networks use 10-100Mbps. | Can’t be used easily between buildings (planning etc). |
| More secure than Wireless. | Not supported on Mobile phones and some tablets. |
Wireless networking uses radio waves to transport data over the air, enabling devices to be connected to a network without any cabling. Wireless LANs are the most well-known and widely deployed form of wireless networking. Alternatives include microwave, satellite, cellular and Bluetooth, among others.
As a general rule, wired networking offers greater speed, reliability and security compared to wireless networks; wireless networking tends to provide more flexibility, mobility and scalability.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Generally easier to set up. | Generally Slower than wired networks. |
| Can be used both on home and public networks. | Limited by range. |
| No cables required. | Open to eavesdropping. |
| Can be used with mobile phones and tablets. | Not as secure depending on set up. |
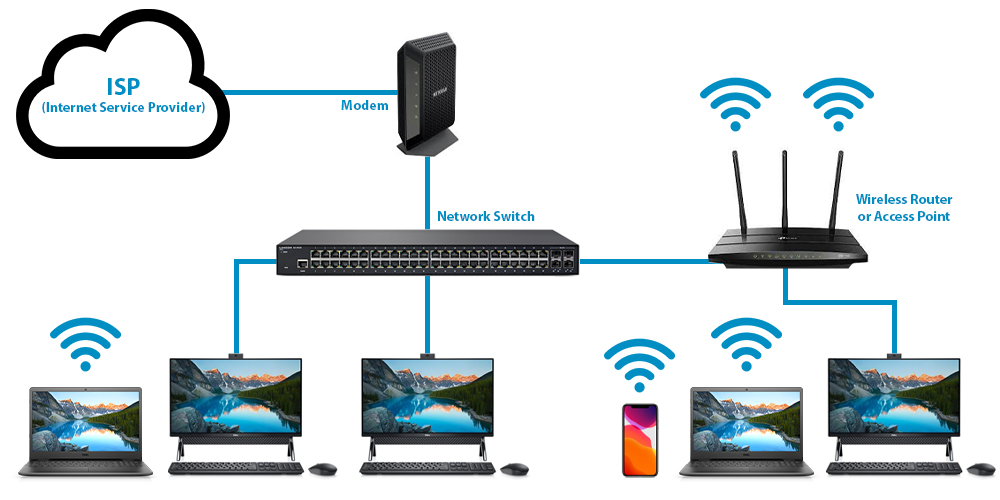
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet, sometimes simply called LAN, is a family of protocols used in wired LANs, described by a set of standards together called IEEE 802.3 published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
What is Internet?
The Internet is the largest example of an internetwork. It is a global system of interconnected governmental, academic, corporate, public, and private computer networks. It is based on the networking technologies of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is the successor of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) developed by DARPA of the United States Department of Defense. The Internet utilizes copper communications and the optical networking backbone to enable the World Wide Web (WWW), the Internet of Things, video transfer and a broad range of information services.
What is wireless LAN?
Wireless LAN, also widely known as WLAN or Wi-Fi, is probably the most well-known member of the IEEE 802 protocol family for home users today. It is standardized by IEEE 802.11 and shares many properties with wired Ethernet.
What is a network switch?
Network switches facilitate the sharing of resources by connecting together all the devices, including computers, printers, and servers, in a small business network. Thanks to the switch, these connected devices can share information and talk to each other, regardless of where they are in a building or on a campus. Building a small business network is not possible without switches to tie devices together.
What is a router?
Just as a switch connects multiple devices to create a network, a router connects multiple switches, and their respective networks, to form an even larger network. These networks may be in a single location or across multiple locations. When building a small business network, you will need one or more routers. In addition to connecting multiple networks together, the router also allows networked devices and multiple users to access the Internet.
What are network topologies?
The term network topology describes the relationship of connected devices in terms of a geometric graph. Devices are represented as vertices, and their connections are represented as edges on the graph. It describes how many connections each device has, in what order, and it what sort of hierarchy.
Typical network configurations include the bus topology, mesh topology, ring topology, star topology, tree topology and hybrid topology.
-
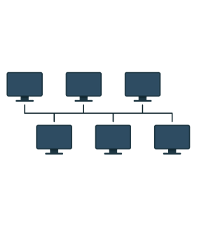
Bus -
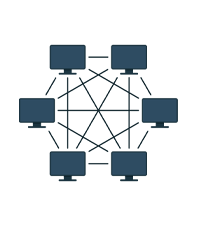
Mesh -
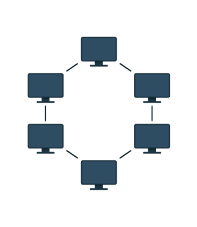
Ring -
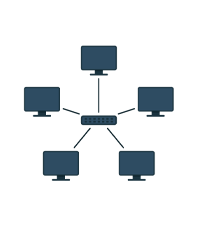
Star -
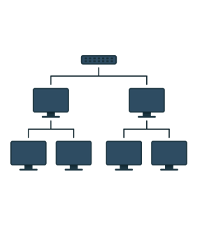
Tree -
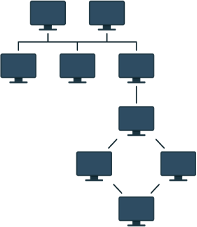
Hybrid
Comprehensive's Comprehensive offers a wide range of Networking Solutions that make it easy to connect to or expand your network. These solutions include Computer Cables, Computer/Network Connectors, Fiber Optic Patch Cables, Laptop Docking Stations, Patch Panels, USB Extenders, USB Hubs and so much more. With Comprehensive, you can always count on 100% uptime.
A: A network is a set or group of devices connected to each other over the physical medium is known as a computer network. For example the Internet.
Q: What do you mean by Network Topology?
A: A network topology is a physical structure of the network which defines how the computers or node will be connected to each other.
Q: What is a Router?
A: A router is a device which is responsible for sending data from source to destination over the computer network.
Q: Describe Hub, Switch and Router?
A: Hub: Hub will broadcast all data to every port. It has a common connection point for all devices.
Switch: Switch will create the dynamic connection and provide information to the requesting port.
Router: Router is the device which will be responsible for forwarding data packets.
Q: What do you mean by the TCP/IP Model?
A: TCP/IP stands for Transmission control protocol and Internet protocol. It describes how the data will get transmitted and routed from end to end communication.
Q: Explain the different Layers of TCP/IP Model.
A: Application Layer, Transport Layer, Network or Internet Layer, Network interface layer.
Q: What do you mean by HTTP?
A: HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol and the port for this is 80. This protocol is responsible for web content.
Q: What do you mean by a Firewall?
A: Firewall is a concept of a security system that helps protect computers from unauthorized access or any cyber-attack.
Q: What do you mean by DNS?
A: DNS Stands for Domain Name System. It’s an internet address mapping process with the local name. We can also call it as an internet phonebook.
Q: What do you mean by Proxy server?
A: Proxy server prevents the external users which are unauthorized to access the network.
Q: What do you mean by Classes of Network?
A: The Classes of IPV4 are of 5 types:
• Class A 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
• Class B 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
• Class C 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
• Class D 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
• Class E 240.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255
Q: What are the types of mode available in Network?
A: Data transferring mode in a computer network will be of three types: Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full Duplex.
Q: What do you mean by Decoder?
A: A decoder is a program which converts the encrypted data into its actual format.
Q: What is an IP address?
A: IP address is the numeric identity of node in network.
Q: What is the difference Static IP address and Dynamic IP address?
A: • A Static IP address is assigned manually. Once assigned it does not change unless it is changed manually again.
• A Dynamic IP address is assigned by a service usually DHCP. It can change any time.
Q: What are the differences between Firewall and Antivirus?
A: • A Firewall filters the incoming network traffic. It is used to secure a system from unauthorized access.
• An Antivirus scans the stored data and installed applications. It is used to secure a system from malware, virus, spyware, adware etc.
Q: What is Encryption?
A: Encryption is the process of converting data in secure form. Once Encrypted, it can’t be read by other devices except the intended receiver.
Q: What is Decryption?
A: Decryption is the process of converting encrypted data back in its original state. In this process first, keys are obtained from the device that encrypted data. Later, these keys are used to decrypt the data. Keys contain the information about how data is encrypted.
Q: What is the Bandwidth?
A: Bandwidth is the amount of data a cable can carry. Bandwidth is computed by subtracting the lower frequency of data signals from the higher one. For digital signal, it is measured in bps (bits per seconds) and for analog signal it is measured in Hz (Hertz).
Q: What is the Telnet?
A: Telnet is a program that allows users to remotely access the system or device in which it is running.
Q: What is a node?
A: A node refers to a point or joint where a connection takes place. It can be a computer or device that is part of a network. Two or more nodes are needed to form a network connection.
Q: What are gateways?
A: Gateways provide connectivity between two or more network segments. It is usually a computer that runs the gateway software and provides translation services. This translation is key in allowing different systems to communicate on the network.
Q: What are MAC addresses?
A: MAC, or Media Access Control, uniquely identifies a device on the network. It is also known as a physical address or an Ethernet address. A MAC address is made up of 6-byte parts.
Q: What is DHCP?
A: DHCP is short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Its main task is to assign an IP address to devices across the network automatically. It first checks for the next available address not yet taken by any device, then assigns this to a network device.
Q: What is Ping?
A: Ping is a utility program that allows you to check connectivity between network devices on the network. You can ping a device by using its IP address or device name, such as a computer name.
Q: What is multicast routing?
A: Multicast routing is a targeted form of broadcasting that sends a message to a selected group of the user instead of sending it to all users on a subnet.
Q: How are IP addresses arranged and displayed?
A: IP addresses are displayed as a series of four decimal numbers that are separated by period or dots. Another term for this arrangement is the dotted-decimal format. An example is 192.168.101.2
Q: Why Use MAC Address?
A: Here are the important reasons for using MAC address:
• It provides a secure way to find senders or receivers in the network.
• MAC address helps you to prevent unwanted network access.
• MAC address is a unique number. Hence it can be used to track the device.
• Wi-Fi networks at the airport use the MAC address of a specific device in order to identify it.
Q: What do you mean by ISP?
A: An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is the industry term for the company that is able to provide you with access to the Internet, typically from a computer. If you hear someone talking about the Internet and they mention their "provider," they're usually talking about their ISP.
Q: Does Comprehensive offer Networking products?
A: Yes, Comprehensive has a huge selection of networking connectivity products including Cat 5e cables, Cat 6 cables, fiber optic patch cords and much more!